
Intel is betting on a new chip substrate material: glass
Intel is betting on a new chip substrate material: glass

Ultra-Thin Glass vs. Super-Thin Glass
Ultra-thin glass (UTG) and super-thin glass represent cutting-edge materials engineering that combines exceptional thinness with remarkable durability and optical performance. These advanced materials have transformed multiple industries, particularly consumer electronics, automotive displays, and medical devices. This comprehensive analysis examines their properties, manufacturing processes, applications, and future potential, highlighting key differences between UTG and super-thin glass technologies.

Borofloat Glass Sheet or EAGLE XG? A Complete Buying Guide
Two names stand out: EAGLE XG and BOROFLOAT 33. They’re used in different ways, and in this guide, we’ll walk through what makes each one special—especially if you’re sourcing materials like a borofloat glass sheet or looking for a custom borosilicate glass solution.
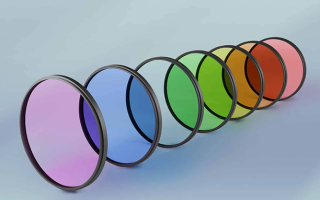
Why Optical Filters Matter—How Quality Glass Makes the Difference
At its core, an optical filter is a device that selectively transmits or blocks specific wavelengths of light. Think of it like sunglasses for your precision optics—except instead of just dimming sunlight, these filters can shape, direct, and fine-tune light in highly specific ways.

Why Glass Polishing Matters More Than You Might Think
When we think about high-quality glass—whether in a telescope lens, a smartphone screen, or a microchip—one thing they all have in common is a flawless, smooth surface. That’s where glass polishing comes in. This crucial process transforms rough, cut, or machined glass into clear, optically refined components with exceptional surface precision. Whether you’re working in optics, semiconductors, or architectural design, understanding how glass is polished helps you appreciate the craftsmanship and technology behind the materials you rely on.

Soda Lime Glass vs Borosilicate Glass: A Comprehensive Comparison
When it comes to selecting the right glass for consumer products, industrial use, or scientific applications, understanding the differences between soda lime glass vs borosilicate glass is essential. These two glass types dominate the market, but they serve different purposes due to their unique chemical compositions, thermal behaviors, and safety profiles.